EcoVadis Carbon Action Manager: Driving supplier emissions transparency and action
EcoVadis Carbon Action Manager: Driving supplier emissions transparency and action
“Simplification and strategic focus in the application of the ESRS empower meaningful sustainability reporting .”
ESRS exposure draft: State of play
What happened?
In July 2025, EFRAG published the revised Exposure Draft of the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS). This revision seeks to simplify sustainability reporting obligations under CSRD in line with the objectives set out by the EU’s Sustainability Omnibus package. The revisions seek to to reduce the overall reporting burden while not jeoparadising interoperability with ISSB’s IFRS S1 and S2 standards
Who will be impacted?
- Companies already subject to CSRD
- Wave 2 and Wave 3 companies (scope discussions TBD under Omnibus I)
- Companies voluntarily reporting under the ESRS
Why were these changes introduced?
Analysis of ESRS-aligned reports revealed hyper-granular, process-oriented approaches to reporting that led to reduced comparability of reports and placed high effort demands on reporting companies. Public feedback called for a reduction in the number and granularity of data points, simplified architecture, clarity, and room for an executive voice.
Simplification levers of the revised ESRS draft
The revised ESRS Draft introduces six key simplification levers designed to balance transparency and burden reduction.
Lever 1: Simplification of Double Materiality Assessment (DMA)
- Challenges: The original check-list approach to the DMA process starting from AR16 requires extensive evidence and detailed analyses, which is resource intensive and hyperfocused on process rather than outcome
- Public Opinion: Calls for a top-down approach focusing on business models and material topics meaningful to users.
- Revised ESRS Draft: Emphasises strategic top-down narrative supported by reasonable and proportionate evidence; removes unnecessary scoring and excessive granularity.
- Impact on Reporters: Enables cohesive story-telling; companies have flexibility to report at topic or sub-topic levels based on relevance.
Lever 2: Better readability and conciseness of sustainability statements and better connectivity with corporate reporting as a whole
- Challenges: Reports were too granular, mixing key information with excessive data points, leading to a compliance exercise rather than strategic communication.
- Public Opinion: excessively complex and granular reporting requirements. Revised ESRS Draft: Introduction of Executive Summary and Appendices, allowing flexibility for executive voice and better alignment with management report format; Impact on Reporters: Easier to produce readable and concise reports aligned with management and financial reporting styles.
Lever 3: Critical modification of the relationship between General Disclosure Requirements in ESRS 2 and topical specifications
- Challenges: Complex and duplicative disclosure requirements between ESRS 2 and topical standards, particularly concerning Policies, Actions, Targets (PATs).
- Public Opinion: Maintain cross-cutting disclosures at ESRS 2 level but reduce duplicate data points at topical level.
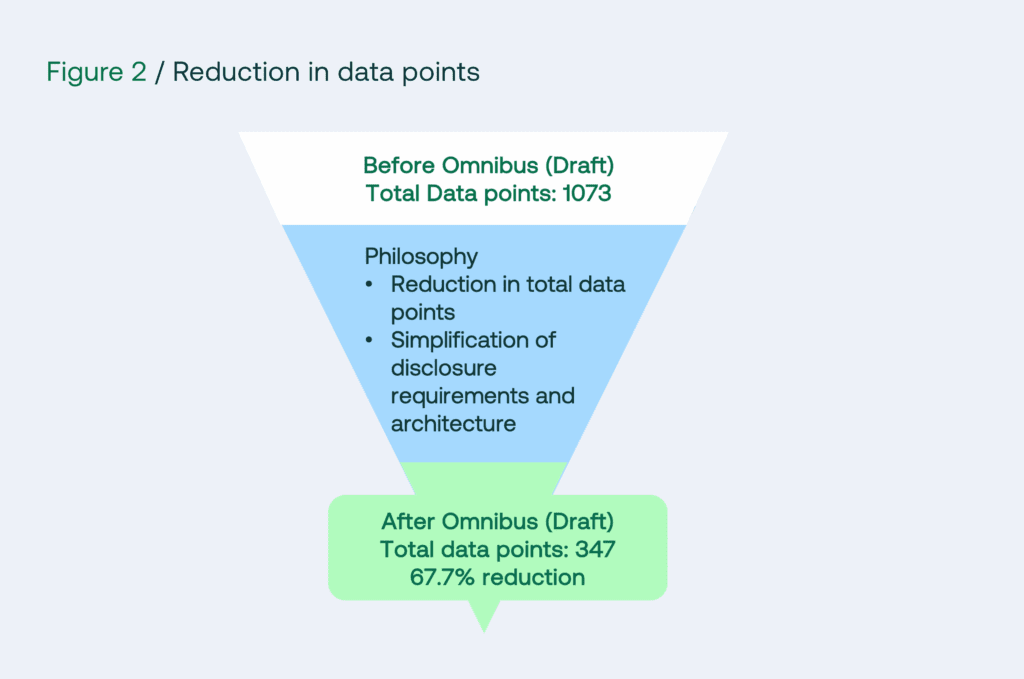
- Revised ESRS Draft: 67.7% reduction in datapoints. Reduces duplication, shifts focus to principle-based approach to narrative disclosures.
- Impact on Reporters: Fewer data points; more effective and less repetitive reporting.
Lever 4: Improved understandability, clarity, and accessibility
- Challenges: Voluntary datapoints created confusion regarding materiality and led to fragmented reporting approaches.
- Public Opinion: Favor complete removal of voluntary datapoints and clearer mandatory versus optional disclosures.
- Revised ESRS Draft: Voluntary datapoints eliminated; mandatory and non-mandatory contents cleanly separated.Impact on Reporters: Simplifies decision-making on what to report; improved transparency.
Lever 5: Introduction of other suggested horizontal burden-reduction reliefs
- Challenges: High effort and burden, especially for smaller entities and those reporting under multiple frameworks, plus resource limitations and commercial sensitivity concerns.
- Public Opinion: Implement relief principles for undue costs, data availability limitations, effort, and flexibility on disclosing anticipated financial effects.
- Revised ESRS Draft: Introduces principle-based reliefs aligning with financial reporting boundaries and stronger interoperability with ISSB standards.
- Impact on Reporters: Practicality and efficiency improvements, especially for SMEs and dual reporters.
Lever 6: Interoperability with ISSB’s IFRS S1 and S2 standards
- Challenges: Divergent requirements between ESRS and other international frameworks caused duplication and fragmentation.
- Public Opinion: Push for terms and principles aligned with IFRS S1/S2 to reduce duplication of efforts .
- Revised ESRS Draft: Aligns language and introduces certain ISSB aligned principles ; shares reliefs and data points where possible. ESRS simplifications sometimes go beyond provisions in ISSB’s IFRS S1 and S2, and some changes even negatively impact interoperability. However, EFRAG states that the Revised ESRS Draft overall increases interoperability.
- Impact on Reporters: Overall reduced effort for companies reporting under multiple regimes; clearer, more consistent sustainability disclosures.
Read our newest reporting guide that tackles various reporting frameworks in relation to one-another. Download below for free!

Questions answered in the webinar
- Will EFRAG suggest a revised methodology for scoring material topics?
- How does the revised ESRS impact companies already reporting under other frameworks like ISSB?
- What are the key challenges companies face with the revised ESRS?
- Are there any changes in the environmental part, such as disclosure for Scope 1, 2 & 3?
- How does the new reporting timeline look like?
Watch the on-demand session to find out more details first hand from our experts.

Reflect and recalibrate
- Sustainability strategy: Is your sustainability strategy properly developed to support the DMA process and sustainability reporting?
- Double materiality assessment: How does your DMA reflect the executive sustainability vision and stakeholder needs?
- Sustainability management systems: Are the right sustainability management systems (Policies, Actions, Targets, and Metrics) in place to facilitate reporting?
Nexio Projects offers consultations to assist organisations in embedding these changes effectively.
How we can support you
Nexio Projects is your full-service sustainability partner. Recognised by Verdantix as a top boutique ESG and sustainability consultancy, we bring clarity to the complexities of your sustainability journey. Our team, including ESG reporting specialists and chartered accountants, supports you in navigating CSRD, ESRS, GRI, VSME, and more.
We assist from reporting compliance to holistic purpose-driven ESG strategies, including:
- Gap analyses and double materiality assessments
- Sustainability strategy development and implementation
- Data collection system design and verification
- Regulatory reporting and audit support
Contact Nexio Projects today for a free consultation or subscribe to our monthly newsletter for sector-specific ESG best practices and updates.